E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
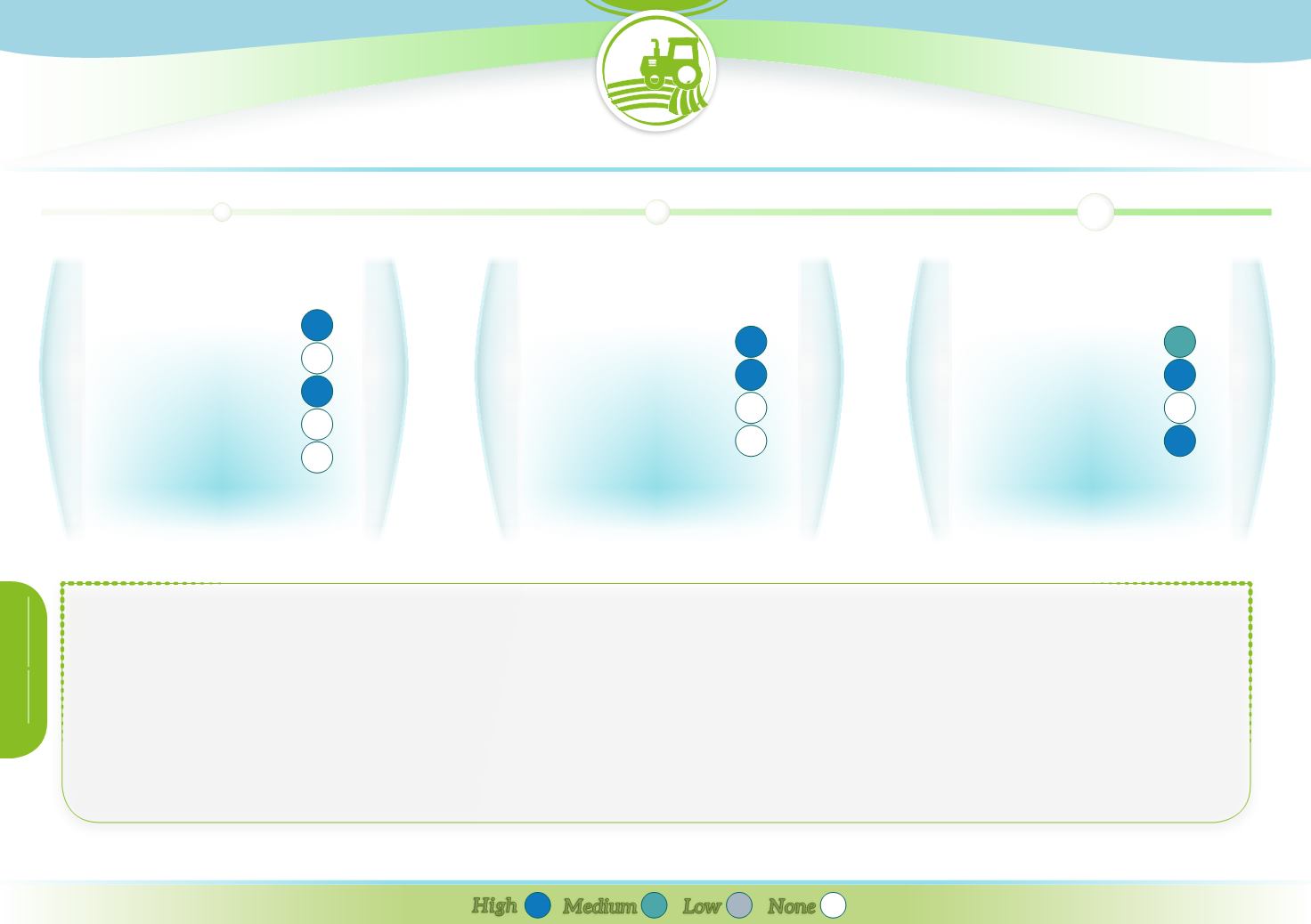
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
By implementing cover crops where the soil would otherwise be left bare (under other crops, between rows) intercropping contributes to increasing
water infiltration
(4
times in Mediterranean vineyards with grass compared to no grass) and
reducing runoff
(20 to 55% in the Sahel compared to sole crops). Reducing runoff and increasing
infiltration provide erosion and sediment control (50% reduction in soil loss in Sahel compared to monoculture). Along with the filtration of pollutants, this helps to address the
WFD objectives
of restoring and maintaining good surface water status. Intercropping also contribute to flood risk reduction and groundwater recharge, and can reduce
wind
erosion
compared to a bare soil.
Intercropping leads to a more stable plant system, a better
soil structure
and improved fertility particularly when it concerns
legumes
. It enables a more efficient use of
resources (light, water, nutrients), thus an increased
productivity
compared with each sole crop of the mixture.
By providing habitats for insects and soil organisms and increasing biodiversity in agro-systems, intercropping make agro-systems
more resilient
. Along with the preservation of
soil fertility, it contributes to maintaining good conditions for further cropping and thus to making agriculture more sustainable


