E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
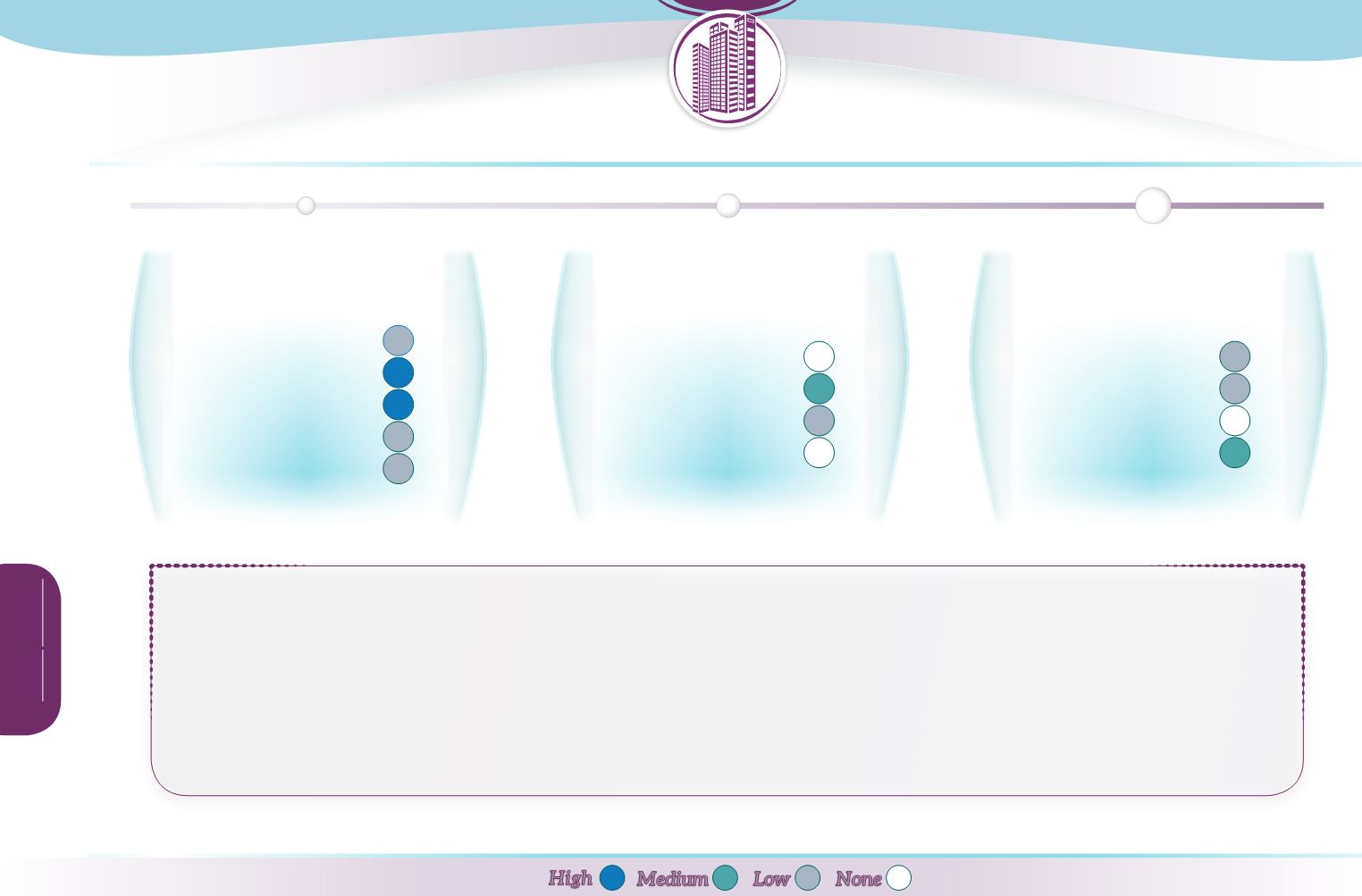
Due to their rough surface, filter strips provide some
slowing of runoff
. In isolation, they provide little benefit in terms of flood risk reduction because they do not store
runoff and provide limited control of peak flow rates. Their contribution to groundwater recharge is also limited due to the short residence time. Filter strips are generally used
as the first stage in a SuDS ‘train’ and in that respect form a component of coordinated
flood risk
management.
Under low to moderate velocities, filter strips effectively
reduce particulate pollutant
levels by removing sediments, organic materials and trace metals from local runoff.
Appropriate design (including slope, width and vegetation type), adequate maintenance and limited fertiliser use are important to achieving high effectiveness. Through contributing
to a reduction in diffuse pollution, filter strips can make a small contribution to preserving and improving
water quality
in receiving waters.
Filter strips introduce
permanent vegetation
to what may otherwise have been an artificial surface or arable land, and thus contribute to creating habitat. They provide an
improvement over traditional drainage and urban land cover regarding green spaces and biodiversity, and may provide some
aesthetic
value. As a
green infrastructure
component, their increased application will provide a small contribution to meeting the objectives of the 2020 Biodiversity Strategy in urban areas.


