E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
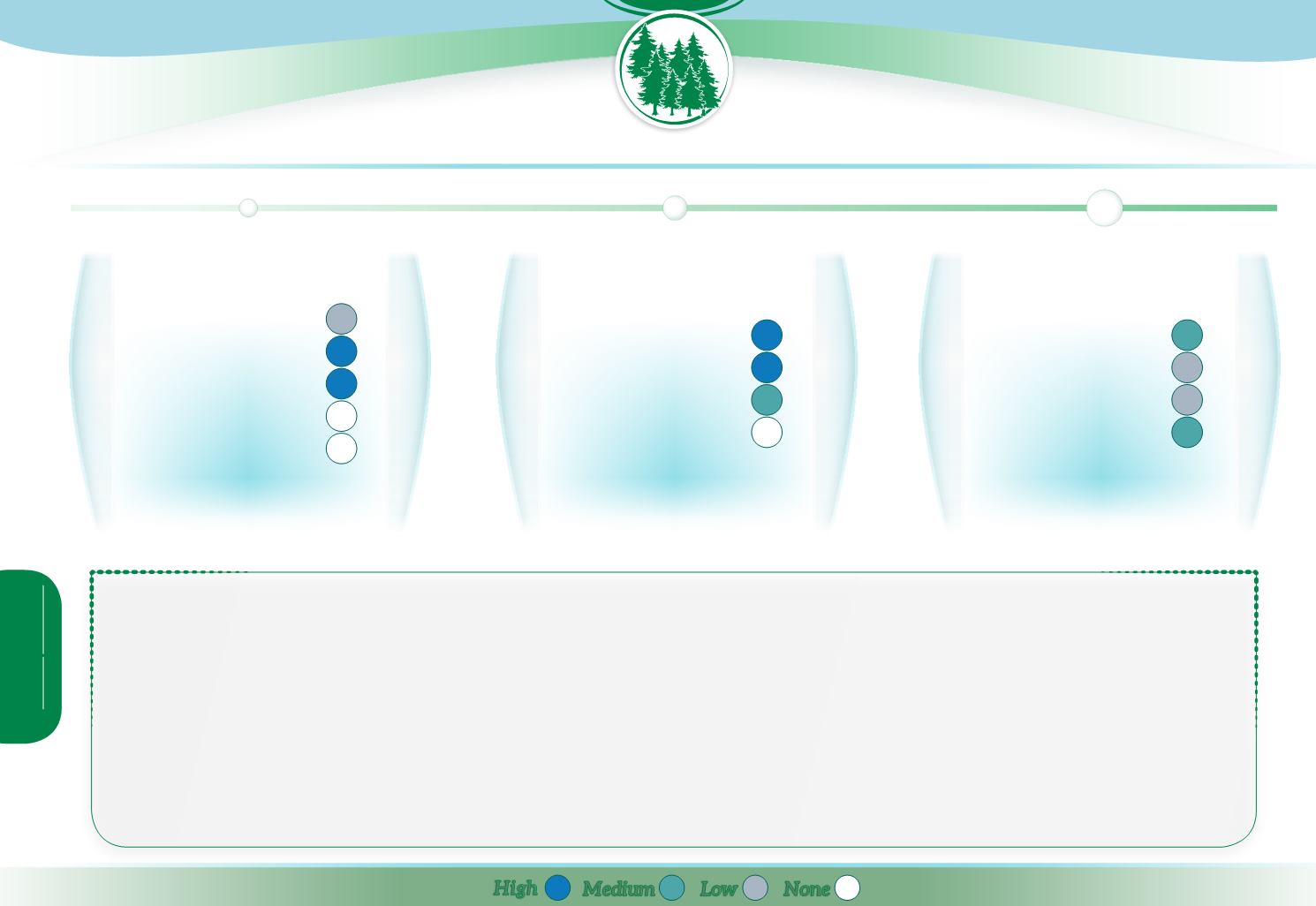
One of the main concerns about ruts and wheel tracks produced when driving heavy forest machinery on sensitive soils is the potential for methylation and mobilization of
mercury.
By preventing it, water sensitive driving contributes to improving the chemical status of priority substances. Since methylmercury bioaccumulates in aquatic food webs,
the measure also contributes to better management of
fish stocks
. Through preventing the concentration of flows in ruts, it contributes to erosion and sediment control during
forestry operations, which also impacts on survival of aquatic organisms.
Water sensitive driving is a
preventative
measure, which when performed properly can prevent water status deterioration. It is likely to have a low to moderate effect on
achievement of WFD policy objectives, largely because of the size
mismatch between the scale
of damage associated with inadequate care to water and the size of WFD
water bodies.
Driving in a manner which does not produce rutting will also help to maintain the
natural hydrologic
behaviour of the forest, the natural infiltration, recharge and soil water
retention properties of forest soils.
Poorly planned and executed driving on wet or fragile soils can leave
unattractive scars
on the landscape which can take many years to recover. Thereby, water sensitive
driving has a positive effect on aesthetic value of forests.


