E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
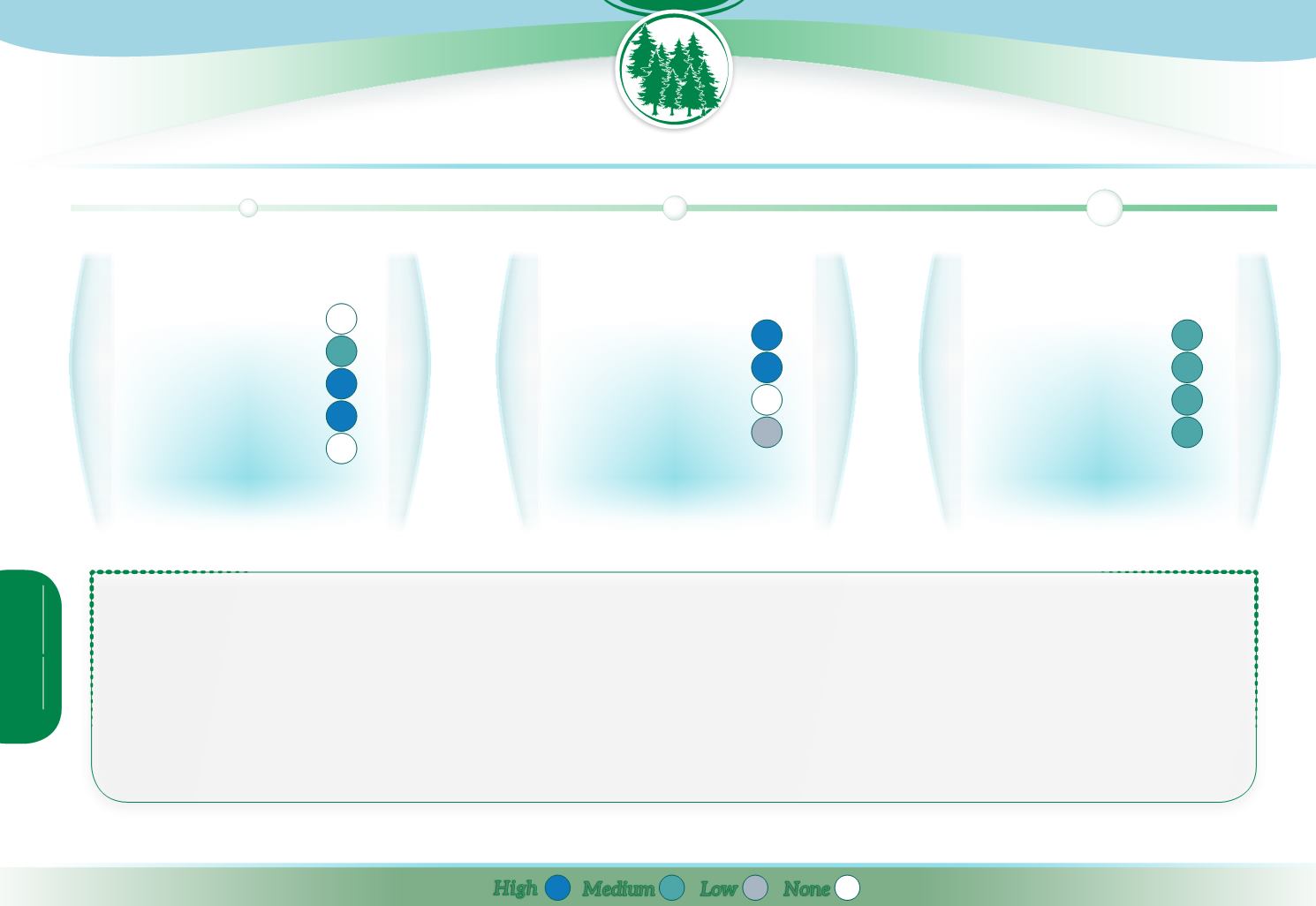
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
When roads and stream crossings in the forest landscape are designed, built and maintained in the correct manner, they have a high potential to
reduce erosion
and control
sediment transport, particularly when unpaved roads are planned to run along contour lines instead of up and down hillslopes. This prevents sediment in runoff from smothering fish
spawning beds and habitat of red list species such as freshwater pearl mussel and can help to
preserve fish stocks
.
It can also help to maintain corridors for aquatic mammals
such as otter and beaver, ensuring aquatic
habitat connectivity
: properly designed stream crossings do not create aquatic habitat
per se
but instead prevent its destruction.
Properly designed road and stream crossings also have the potential to reduce mobilisation of sediment-associated pollutants including phosphorus. The measure has a high potential
for preventing
surface water status
deterioration, protecting both biological and chemical quality elements.
Appropriately designed stream crossings can contribute to a reduction in flood risk. Poorly designed crossings which constrict high flows can lead to
localised flooding
upstream
of the stream crossing.
In the case of larger streams and small rivers, it is possible that poorly designed stream crossings could impede navigation. They can also be dangerous for recreational watercrafts.


