Project funded
by theEU–DGEnvironment
L
andsurfacerelevant
forapplication
Artificial surface
Agriculture land
Forest and semi-natural areas
Wetlands
F
inancialcosts
(C
apital
,
operation
&
maintenance
)
The costs can vary considerably depending on the type of mechanism and the
scale. The case study in Los Arenales, Segovia, provides information on costs linked
to restoration of reference condition infiltration for a 3ha infiltration zone: M€0.6
(investigation and studies); M€0.4 (water intake); M€2.5 (transfer conveyance);
M€0.9 (recharge channel).
D
esign
The design will vary considerably depending on the type of mechanism used for
recharge, so site-specific consideration is necessary. Depending on the type of
infiltration features and the source of the water, pre-treatment may be necessary
to
prevent pollution
from reaching groundwater.
This type of measure overlaps with a range of other measures that provide
infiltration to groundwater by various means.
S
cale
Upstream drainage area can be any
scale, ranging from a single plot to large
catchments greater than 1000km2.
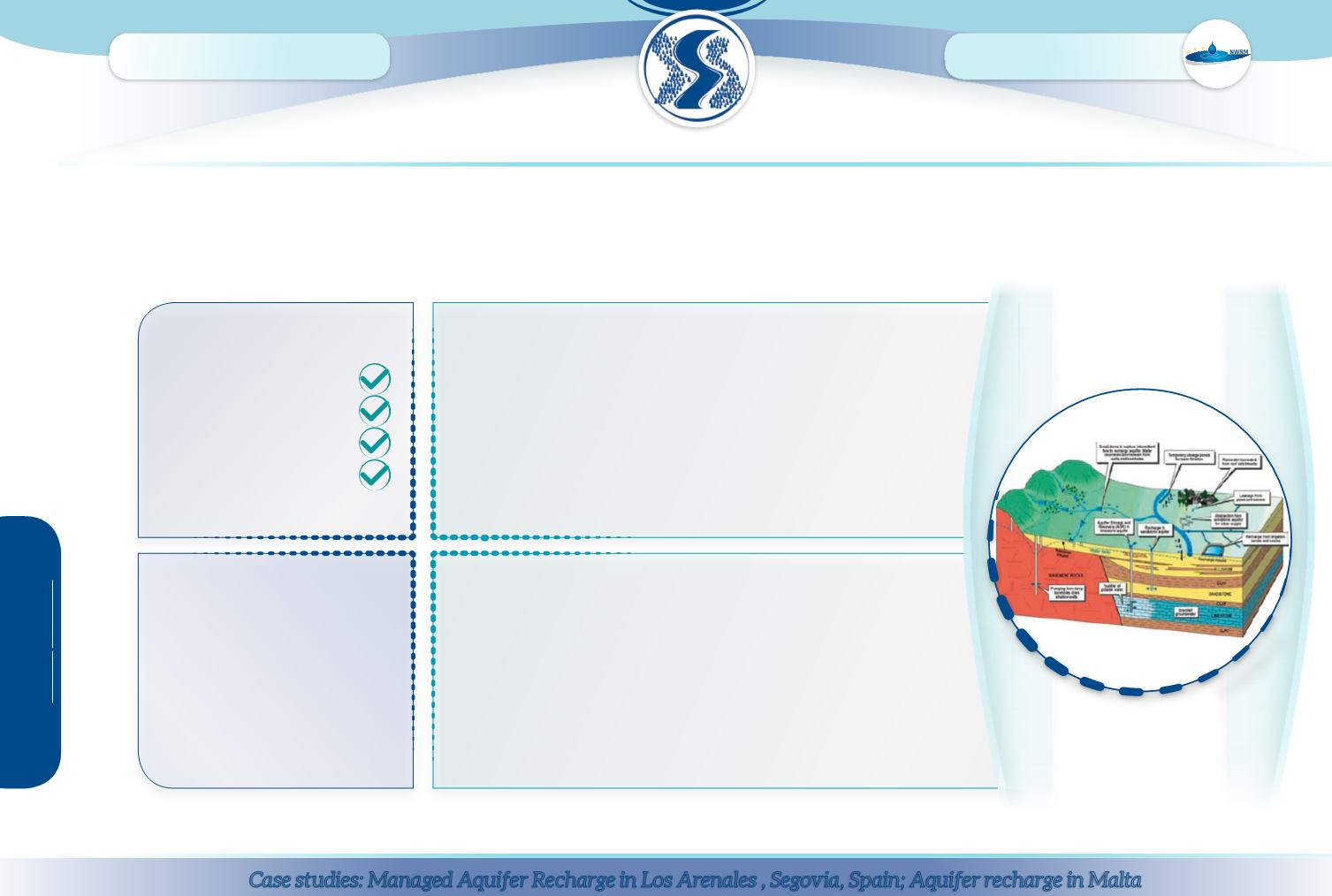
Restoration of natural infiltration to groundwater, also known as “Artificial Groundwater Recharge” in the engineering literature, can include: (i)
surface
structures
to facilitate/augment recharge (such as soakaways and infiltration basins); (ii)
subsurface indirect recharge
– infiltration capacity is enhanced
through wells drilled within the unsaturated zone; and (iii) subsurface direct recharge – infiltration and recharge of the groundwater aquifer is accomplished
through wells reaching the saturated zone.
Case studies:ManagedAquiferRecharge inLosArenales , Segovia, Spain;Aquifer recharge inMalta
HYDROMORPHOLOGY
©
w
w
w
.
bg
s
.
a
c
.
u
k


