E
cosystem
servicesdelivered
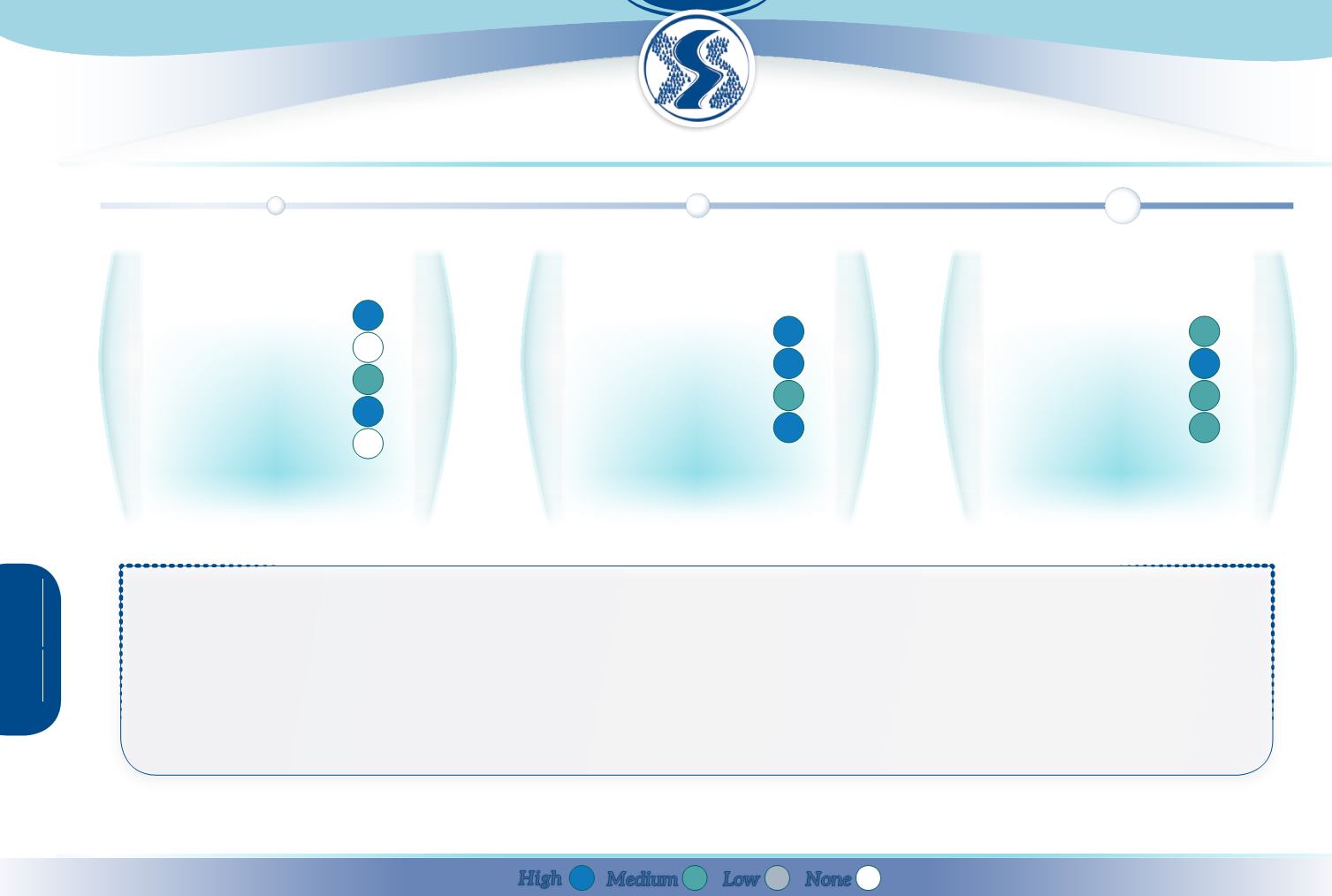
Provisioning
Regulation & maintenance
Cultural
Abiotic
C
ontribution
topolicyobjectives
Water Framework Directive
Floods Directive
Birds & Habitats Directive
2020 Biodiversity Strategy
P
otential
biophysicaleffects
Runoff
Reducing pollution
Soil conservation
Habitat
Climate Change
High
Low
Medium
None
Renaturalisation of polder areas has a significant impact on
river water storage
(water is stored in watercourses and hydraulic annexes inside of the polder instead of being
pumped out of the polder). It also has a positive impact on infiltration and soil water retention. Flood retention areas such as polders provide cost-effective protection against
flood
damage, with additional ecological benefits as a result of renaturalisation measures.
Ecological flooding
contributes to raising
groundwater levels
, including outside of the polder. Due to ecological flooding, soils inside renaturalised polders are constantly
enriched by organic sediments, which serve as fertiliser for plants.
Water courses in renaturalised polders can provide habitat for a variety of invertebrate and fish species, and thus enhance fish stocks. In some cases, ground beetle and dragonfly
species can establish in alluvial forests. However it is possible that populations of mosquitos and other pests could also increase, with negative consequences for the nearby human
populations. Renaturalised polders also have
cultural value
, for example in the Netherlands, where they act as recreational areas.


